计算机保研复习-算法基础课(java&&C++)
算法基础课(java&&C++)

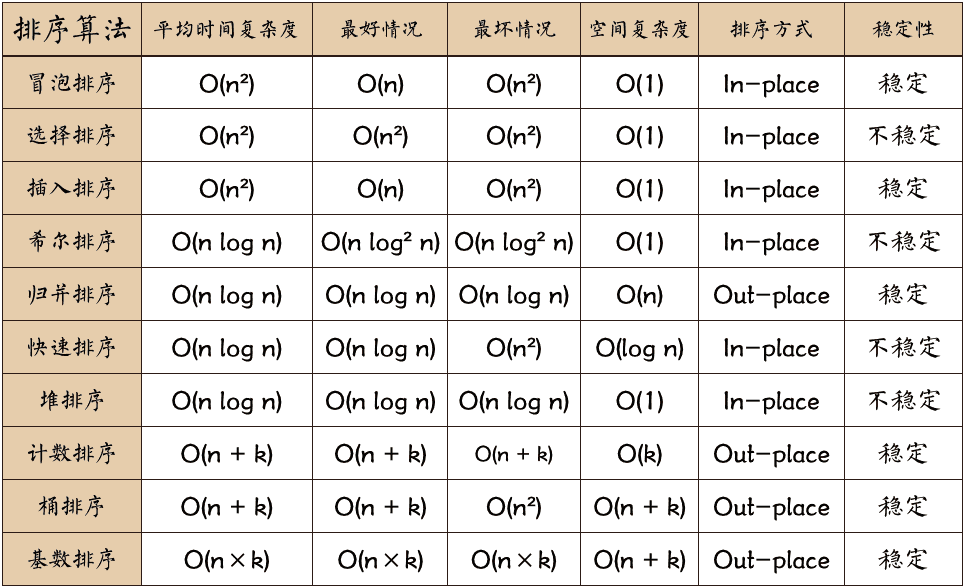
第一章 基础算法
1.1 快速排序
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
const int N = 1000010;
int q[N];
void quick_sort(int l, int r){
if (l >= r) return;
int i = l - 1, j = r + 1, x = q[l + r >> 1];
while (i < j){
do i ++ ; while (q[i] < x);
do j -- ; while (q[j] > x);
if (i < j) swap(q[i], q[j]);
}
quick_sort(l, j);
quick_sort(j + 1, r);
}
int main(){
int n;
scanf("%d", &n);
for (int i = 0; i < n; i ++ ) scanf("%d", &q[i]);
quick_sort(0, n - 1);
for (int i = 0; i < n; i ++ ) printf("%d ", q[i]);
return 0;
}
1.2 归并排序
1.2.1 归并排序
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
const int N = 1e6 + 10;
int a[N], tmp[N];
void merge_sort(int q[], int l, int r){
if (l >= r) return;
int mid = l + r >> 1;
merge_sort(q, l, mid), merge_sort(q, mid + 1, r);
int k = 0, i = l, j = mid + 1;
while (i <= mid && j <= r)
if (q[i] <= q[j]) tmp[k++] = q[i++];
else tmp[k++] = q[j++];
while (i <= mid) tmp[k++] = q[i++];
while (j <= r) tmp[k++] = q[j++];
for (i = l, j = 0; i <= r; i ++, j ++ ) q[i] = tmp[j];
}
int main(){
int n;
scanf("%d", &n);
for (int i = 0; i < n; i ++ ) scanf("%d", &a[i]);
merge_sort(a, 0, n - 1);
for (int i = 0; i < n; i ++ ) printf("%d ", a[i]);
return 0;
}
1.2.2 逆序对的数量
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
const int N = 100010;
int a[N], tmp[N];
typedef long long LL;
LL merge_sort(int l, int r) {
if (l >= r) return 0;
int mid = l + r >> 1;
LL res = merge_sort(l, mid) + merge_sort(mid + 1, r);
int k = 0, i = l, j = mid + 1;
while (i <= mid && j <= r) {
if (a[i] <= a[j]) tmp[k++] = a[i++];
else tmp[k++] = a[j++], res += mid - i + 1;
}
while (i <= mid) tmp[k++] = a[i++];
while (j <= r) tmp[k++] = a[j++];
for (i = l, j = 0; i <= r; i++) a[i] = tmp[j++];
return res;
}
int main() {
int n;
cin >> n;
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) cin >> a[i];
cout << merge_sort(0, n - 1) << endl;
}
1.3 二分
1.3.1 整数二分
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
const int N = 100010;
int q[N];
int findL(int l, int r, int x) {
while (l < r) {
int m = l + r >> 1;
if (q[m] >= x) r = m;
else l = m + 1;
}
return l;
}
int findR(int l, int r, int x) {
while (l < r) {
int m = l + r + 1 >> 1;
if (q[m] <= x) l = m;
else r = m - 1;
}
return l;
}
int main() {
int n, m;
scanf("%d%d", &n, &m);
for (int i = 0; i < n; ++i) scanf("%d", &q[i]);
while (m--) {
int x;
scanf("%d", &x);
int l = findL(0, n - 1, x);
if (q[l] != x) cout << "-1 -1" << endl;
else {
cout << l << " ";
cout << findR(0, n - 1, x) << endl;
}
}
return 0;
}
1.3.2 小数二分
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
int main() {
double n;
int f = 0;
cin >> n;
if (n < 0) {
n = -n;
f = 1;
}
double l = 0, r = 100;
while (r - l > 1e-8) {
double mid = (l + r) / 2;
if (mid * mid * mid < n) l = mid;
else r = mid;
}
if (f == 1) printf("%.6f", -l);
else printf("%.6f", l);
}
1.4 位运算
lowbit:是非负整数 n 在二进制表示下最低位的 1 及其后面的所有的 0 的二进制构成的数值。
求1的个数:
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
int lowbit(int x) {
return x & -x;
}
int main() {
int n;
cin >> n;
while (n--) {
int x, res = 0;
cin >> x;
while (x) {
x -= lowbit(x);
res++;
}
cout << res << " ";
}
}
n >> x : 右移x位 &1 看看是不是1 n^1 <<x :如果ab不同异或1等同于取反
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
int main() {
int n, x, y;
cin >> n >> x >> y;
int a = n >> x & 1, b = n >> y & 1;
if (a != b) {
n ^= 1 << x;
n ^= 1 << y;
}
cout << n;
}
1.5 前缀和与差分
1.5.1 前缀和
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
const int N = 100010;
int a[N];
int main() {
int n, m;
cin >> n >> m;
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++) {
int t;
cin >> t;
a[i] = t + a[i - 1];
}
while (m--) {
int l, r;
cin >> l >> r;
cout << a[r] - a[l - 1] << endl;
}
}
1.5.2 子矩阵的和
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
const int N = 1010;
int n, m, q;
int s[N][N];
int main() {
cin >> n >> m >> q;
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++)
for (int j = 1; j <= m; j++)
scanf("%d", &s[i][j]);
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++) {
for (int j = 1; j <= m; j++) {
s[i][j] += s[i - 1][j] + s[i][j - 1] - s[i - 1][j - 1];
}
}
while (q--) {
int x1, y1, x2, y2;
scanf("%d%d%d%d", &x1, &y1, &x2, &y2);
printf("%d\n", s[x2][y2] - s[x1 - 1][y2] - s[x2][y1 - 1] + s[x1 - 1][y1 - 1]);
}
}
1.5.3 差分
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
const int N = 100010;
int a[N], b[N];
void insert(int l, int r, int c) {
b[l] += c;
b[r + 1] -= c;
}
int main() {
int n, m;
cin >> n >> m;
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++) scanf("%d", &a[i]);
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++) insert(i, i, a[i]);
while (m--) {
int l, r, c;
scanf("%d%d%d", &l, &r, &c);
insert(l, r, c);
}
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++) b[i] += b[i - 1];
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++) printf("%d ", b[i]);
return 0;
}
1.5.4 差分矩阵
java
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
const int N = 1010;
int a[N][N], b[N][N];
void insert(int x1, int y1, int x2, int y2, int c) {
b[x1][y1] += c;
b[x2 + 1][y1] -= c;
b[x1][y2 + 1] -= c;
b[x2 + 1][y2 + 1] += c;
}
int main() {
int n, m, q;
cin >> n >> m >> q;
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++){
for (int j = 1; j <= m; j++) {
cin >> a[i][j];
insert(i, j, i, j, a[i][j]);
}
}
while (q-- != 0) {
int x1, x2, y1, y2, c;
cin >> x1 >> y1 >> x2 >> y2 >> c;
insert(x1, y1, x2, y2, c);
}
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++) {
for (int j = 1; j <= m; j++) {
a[i][j] = a[i][j - 1] + a[i - 1][j] - a[i - 1][j - 1] + b[i][j];
cout << a[i][j] << " ";
}
cout << endl;
}
}
1.6 双指针
1.6.1 最长连续不重复子序列
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
const int N = 100010;
int a[N], cnt[N];
int main() {
int n, res = 0;
cin >> n;
for (int i = 0,j = 0 ; i < n; i++) {
cin >> a[i];
cnt[a[i]]++;
while (cnt[a[i]] > 1) cnt[a[j++]]--;
res = max(res, i - j + 1);
}
cout << res << endl;
}
1.6.2 数组元素和
#include <iostream>
#include <cstring>
#include <algorithm>
#include <unordered_map>
using namespace std;
const int N = 100010;
int n, m, x;
int a[N], b[N];
unordered_map<int, int> h;
int main() {
cin >> n >> m >> x;
for (int i = 0; i < n; i ++) {
cin >> a[i];
h[a[i]] = i;
}
for (int i = 0; i < m; i ++) {
cin >> b[i];
if (h.count(x - b[i])) cout << h[x - b[i]] << " " << i << endl;
}
return 0;
}
1.6.3 判断子序列
import java.util.Scanner;
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);
int n = sc.nextInt();
int m = sc.nextInt();
int[] a = new int[n];
int[] b = new int[m];
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) a[i]= sc.nextInt();
for (int i = 0; i < m; i++) b[i]= sc.nextInt();
for (int j = 0,i = 0; j < m; j++) if (i < n && b[j] == a[i]) i++;
if (i == n) System.out.println("Yes");
else System.out.println("No");
}
}
1.7 区间合并
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.Comparator;
import java.util.Scanner;
public class acwing803 {
static ArrayList<int[]> arrayList = new ArrayList<int[]>();
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);
int n = sc.nextInt();
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
int[] lr = new int[2];
lr[0]=sc.nextInt();;
lr[1]=sc.nextInt();
arrayList.add(lr);
}
System.out.println(merge());
}
static int merge(){
ArrayList<int[]> res = new ArrayList<int[]>();
arrayList.sort(new Comparator<int[]>() {
@Override
public int compare(int[] o1, int[] o2) {
return o1[0] - o2[0];
}
});
int l = Integer.MIN_VALUE;
int r = Integer.MIN_VALUE;
// int l = arrayList.get(0)[0];
// int r = arrayList.get(0)[1];
for (int[] temp : arrayList) {
if (temp[0] > r){
if (l != Integer.MIN_VALUE) res.add(new int[]{l,r});
// res.add(new int[]{l,r});
l = temp[0];
r = temp[1];
}else r = Math.max(r,temp[1]);
}
if (l!= Integer.MIN_VALUE) res.add(new int[]{l,r});
// res.add(new int[]{l,r});
return res.size();
}
}
#include <iostream>
#include <vector>
#include <algorithm>
using namespace std;
typedef pair<int, int> PII;
vector<PII> v, res;
void merge() {
int l = v[0].first, r = v[0].second;
for (auto a : v) {
if (a.first > r) {
res.push_back({ l,r });
l = a.first;
r = a.second;
}
else r = max(r, a.second);
}
res.push_back({ l,r });
}
int main() {
int n;
cin >> n;
while (n--) {
int l, r;
cin >> l >> r;
v.push_back({ l,r });
}
sort(v.begin(), v.end());
merge();
cout << res.size() << endl;
}
多路归并
acwing 1262
import java.util.Comparator;
import java.util.PriorityQueue;
import java.util.Queue;
import java.util.Scanner;
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);
int n = sc.nextInt();
int[] a = new int[n];
int[] b = new int[n];
int[] c = new int[n];
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) a[i] = sc.nextInt();
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) b[i] = sc.nextInt();
for (int i = 1; i < n; i++) c[i] = c[i-1] + sc.nextInt();
int res = -1, T = sc.nextInt();
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
int fishTime = T - c[i];
PriorityQueue<Node> q = new PriorityQueue<>(new Comparator<Node>() {
@Override
public int compare(Node o1, Node o2) {
return o2.num-o1.num;
}
});
int fish = 0;
for (int j = 0; j <= i; j++) q.offer(new Node(j,a[j]));
while (!q.isEmpty() && fishTime > 0){
Node top = q.poll();
fish += top.num;
fishTime--;
top.num-=b[top.id];
if (top.num > 0) q.offer(top);
}
res = Math.max(res,fish);
}
System.out.println(res);
}
static class Node{
int id,num;
Node(int id,int num){
this.id=id;
this.num=num;
}
}
}
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
const int N = 100010;
int a[N],b[N];
int n,m;
typedef long long LL;
typedef pair<int,int>PII;
#define x first
#define y second
priority_queue<PII>heap;
int main(){
cin>>n>>m;
for (int i=1;i<=n;i++) {
cin>>a[i]>>b[i];
heap.push({a[i],i});
}
LL ans = 0;
while (m--){
ans+=heap.top().x;
int id = heap.top().y;
heap.pop();
a[id]-=b[id];
heap.push({a[id],id});
}
cout<<ans<<endl;
return 0;
}
日期问题
import java.util.Scanner;
public class acwing3498 {
static int dates[] = {0,31,28,31,30,31,30,31,31,30,31,30,31};
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);
for (int i = 1; i < dates.length; i++) dates[i] += dates[i-1];
while (sc.hasNext()){
String s1 = sc.next();
String s2 = sc.next();
int date1 = transform(s1);
int date2 = transform(s2);
System.out.println(Math.abs(date2-date1)+1);
}
}
static int transform(String s){
int year = Integer.parseInt(s.substring(0, 4));
int month = Integer.parseInt(s.substring(4, 6));
int date = Integer.parseInt(s.substring(6, 8));
int sumYear = 365 * year + (year - 1) / 4 - (year - 1) / 100 + (year - 1) / 400;
int sumMonth = dates[month - 1];
if (((year % 4 == 0 && year % 100 != 0) || year % 400 == 0 ) && month > 2) sumMonth++;
return sumYear+sumMonth+date;
}
}
/**
* import java.time.LocalDate;
* import java.time.format.DateTimeFormatter;
* import java.time.temporal.ChronoUnit;
* import java.util.Scanner;
*
* public class DateDifference {
* public static void main(String[] args) {
* Scanner scanner = new Scanner(System.in);
* DateTimeFormatter formatter = DateTimeFormatter.ofPattern("yyyyMMdd");
*
* while (scanner.hasNext()) {
* String dateString1 = scanner.next();
* String dateString2 = scanner.next();
*
* LocalDate date1 = LocalDate.parse(dateString1, formatter);
* LocalDate date2 = LocalDate.parse(dateString2, formatter);
*
* long difference = ChronoUnit.DAYS.between(date1, date2);
* System.out.println(Math.abs(difference) + 1); // 加一是因为题目规定连续日期之间的差值为2天
* }
*
* scanner.close();
* }
* }
*/
第二章 数据结构
2.1 单链表
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
const int N = 100010;
int n;
int h[N], e[N], ne[N], head, idx;
void init(){
head = -1;
idx = 0;
}
void int_to_head(int x){
e[idx] = x;
ne[idx] = head;
head = idx++;
}
void add(int k, int x){
e[idx] = x;
ne[idx] = ne[k];
ne[k] = idx++;
}
void remove(int k){
ne[k] = ne[ne[k]];
}
int main(){
cin >> n;
init();
for (int i = 0; i < n; i ++ ) {
char s;
cin >> s;
if (s == 'H') {
int x;
cin >> x;
int_to_head(x);
}
if (s == 'D'){
int k;
cin >> k;
if (k == 0) head = ne[head];
else remove(k - 1);
}
if (s == 'I'){
int k, x;
cin >> k >> x;
add(k - 1, x);
}
}
for (int i = head; i != -1; i = ne[i]) cout << e[i] << ' ' ;
cout << endl;
return 0;
}
2.2 双链表
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
const int N = 1e5 + 10;
int m;
int e[N], l[N], r[N];
int idx;
void init(){
l[1] = 0, r[0] = 1;//* 初始化 第一个点的右边是 1 第二个点的左边是 0
idx = 2;//! idx 此时已经用掉两个点了
}
void add(int k, int x){
e[idx] = x;
l[idx] = k;
r[idx] = r[k];
l[r[k]] = idx;
r[k] = idx++;
}
void remove(int k){
r[l[k]] = r[k];
l[r[k]] = l[k];
}
int main(void){
ios::sync_with_stdio(false);
cin >> m;
init();
while(m--) {
string op;
cin >> op;
int k, x;
if(op=="R"){
cin >> x;
add(l[1], x); //! 0和 1 只是代表 头和尾 所以 最右边插入 只要在 指向 1的 那个点的右边插入就可以了
}
else if(op=="L")//! 同理 最左边插入就是 在指向 0的数的左边插入就可以了 也就是可以直接在 0的 有右边插入
{
cin >> x;
add(0, x);
}
else if(op=="D"){
cin >> k;
remove(k + 1);
}
else if(op=="IL"){
cin >> k >> x;
add(l[k + 1], x);
}
else{
cin >> k >> x;
add(k + 1, x);
}
}
for(int i = r[0]; i != 1; i = r[i]) cout << e[i] << ' ';
return 0;
}
2.3 模拟栈
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
const int N = 100010;
int st[N];
int top = -1;
int n;
int main(){
cin >> n;
while(n--){
string s;
cin >> s;
if(s == "push"){
int a;
cin >> a;
st[++top] = a;
}
if(s == "pop") top --;
if(s == "query") cout << st[top] << endl;
if(s == "empty") cout << (top == -1 ? "YES" : "NO") << endl;
}
}
栈运算
#include <iostream>
#include <string>
#include <stack>
#include <unordered_map>
using namespace std;
stack<char> op;
stack<int> num;
unordered_map<char, int> pr = {{'+', 1}, {'-', 1}, {'*', 2}, {'/', 2}};
void eval(){
int b = num.top(); num.pop();
int a = num.top(); num.pop();
char c = op.top(); op.pop();
int x;
if(c == '+') x = a + b;
else if(c == '-') x = a - b;
else if(c == '*') x = a * b;
else x = a / b;
num.push(x);
}
int main(){
string s;
cin >> s;
for(int i = 0; i < s.size(); i++){
char c = s[i];
if(isdigit(c)){
int x = 0, j = i;
while(j < s.size() && isdigit(s[j])) x = 10 * x + s[j++] - '0';
i = j - 1;
num.push(x);
}
else if(c == '(') op.push(c);
else if(c == ')') {
while(op.size() && op.top() != '(') eval();
op.pop();
}
else {
while(op.size() && pr[op.top()] >= pr[c]) eval();
op.push(c);
}
}
while(op.size()) eval();
cout << num.top() << endl;
return 0;
}
2.4 模拟队列
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
const int N = 100010;
int q[N];
//[hh, tt] 之间为队列(左闭右闭)
int hh = 0;//队头位置
int tt = -1;//队尾位置
int m;
string s;
void push(int x){
q[++tt] = x;
}
void pop(){
hh++;
}
//当tt >= hh时,区间不为空
void empty(){
if(tt >= hh) cout << "NO" << endl;
else cout << "YES" << endl;
}
void query (){
cout << q[hh] << endl;
}
int main(){
cin >> m;
while(m--){
cin >> s;
if(s == "push"){
int x;
cin >> x;
push(x);
}
if(s == "pop") pop();
if(s == "empty") empty();
if(s == "query") query();
}
}
2.5 单调栈
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
const int N = 100010;
int stk[N], tt;
int main(){
int n;
cin >> n;
while (n-- ){
int x;
scanf("%d", &x);
while (tt && stk[tt] >= x) tt -- ;
if (!tt) printf("-1 ");
else printf("%d ", stk[tt]);
stk[++tt] = x;
}
return 0;
}
2.6 单调队列
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
const int N = 1e6+10;
int n,k;
int a[N],q[N];//队列q不是滑动窗口!只是在实际窗口向右滑动时维护的一个单调队列。队列q的放置方式:hh队头在左端,tt队尾在右
int hh,tt=-1;
int main(){
cin >> n >> k;
for(int i=0;i<n;i++) scanf("%d", &a[i]);
//找窗口中的最小值
for(int i=0;i<n;i++){
//其中i表示滑动窗口的右端点位置,所以当前实际窗口的左端点位置应为i-k+1
//而队列q[hh]存的则为窗口中数值最小的元素的位置,姑且记为pos,
//则必有pos>=i-k+1,反之(即i-k+1>pos),则pos位置已经从左边移出窗口,
//而位置pos即为q[hh],故若i-k+1>pos,则hh++;
if(hh<=tt&&i-k+1>q[hh]) hh++;
//若队尾元素的值a[q[tt]]>=滑动窗口的右端点a[i],则为了维护队列q单调,需要删除队尾
while(hh<=tt&&a[q[tt]]>=a[i]) tt--;
//直到队尾元素比窗口右端点的值小a[q[tt]]<a[i],将位置i入队
q[++tt] = i;
//窗口是从数组a中第一个元素a[0]开始吞入,故要等到窗口中的元素满了才可以输出。
if(i>=k-1) printf("%d ",a[q[hh]]);
}
printf("\n");
//找窗口中的最大值
hh = 0, tt = -1;
for(int i=0;i<n;i++){
if(hh<=tt&&i-k+1>q[hh])hh++;
while(hh<=tt&&a[q[tt]]<=a[i])tt--;//只需要修改这里的
q[++tt]=i;
if (i>=k -1)printf("%d ", a[q[hh]]);
}
return 0;
}
2.7 KMP
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
const int N = 100010, M = 1000010;
int n, m;
int ne[N];
char s[M], p[N];
int main(){
cin >> n >> p + 1 >> m >> s + 1;
for (int i = 2, j = 0; i <= n; i ++ ) {
while (j && p[i] != p[j + 1]) j = ne[j];
if (p[i] == p[j + 1]) j ++ ;
ne[i] = j;
}
for (int i = 1, j = 0; i <= m; i ++ ) {
while (j && s[i] != p[j + 1]) j = ne[j];
if (s[i] == p[j + 1]) j ++ ;
if (j == n)
{
printf("%d ", i - n);
j = ne[j];
}
}
return 0;
}
import java.io.BufferedReader;
import java.io.BufferedWriter;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.io.InputStreamReader;
import java.io.OutputStreamWriter;
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) throws NumberFormatException, IOException {
BufferedReader reader = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(System.in));
BufferedWriter writer = new BufferedWriter(new OutputStreamWriter(System.out));
int n = Integer.parseInt(reader.readLine());
// 模式串p
String P = reader.readLine();
char[] p = new char[n + 1];
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++) p[i] = P.charAt(i - 1);
int m = Integer.parseInt(reader.readLine());
String S = reader.readLine();
char[] s = new char[m + 1];
for (int i = 1; i <= m; i++) s[i] = S.charAt(i - 1);
int prefix[] = new int[n + 1];
for (int i = 2, j = 0; i <= n; i++) {
while (j != 0 && p[i] != p[j + 1])j = prefix[j];
if (p[i] == p[j + 1])j++;
prefix[i] = j;
}
for (int i = 1, j = 0; i <= m; i++) {
while (j != 0 && s[i] != p[j + 1]) j = prefix[j];
if (s[i] == p[j + 1]) j++;
if (j == n) {
writer.write(i - n +" ");
j = prefix[j];
}
}
writer.flush();
writer.close();
reader.close();
}
}
2.8 Trie树
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
const int N = 100010;
//son[][]存储子节点的位置,分支最多26条;
//idx表示当前要插入的节点是第几个,每创建一个节点值+1
int son[N][26], cnt[N], idx;
char str[N];
void insert(char *str){
int p = 0;
for(int i = 0; str[i]; i++) {
int u = str[i] - 'a';
if(!son[p][u]) son[p][u] = ++idx; //该节点不存在,创建节点
p = son[p][u]; //使“p指针”指向下一个节点
}
cnt[p]++;
}
int query(char *str) {
int p = 0;
for(int i = 0; str[i]; i++)
{
int u = str[i] - 'a';
if(!son[p][u]) return 0; //该节点不存在,即该字符串不存在
p = son[p][u];
}
return cnt[p]; //返回字符串出现的次数
}
int main(){
int m;
cin >> m;
while(m--) {
char op[2];
scanf("%s%s", op, str);
if(*op == 'I') insert(str);
else printf("%d\n", query(str));
}
return 0;
}
#include<iostream>
#include<algorithm>
using namespace std;
int const N=100010,M=31*N;
int n;
int a[N];
int son[M][2],idx;
void insert(int x){
int p=0; //根节点
for(int i=30;i>=0;i--){
int u=x>>i&1; //取X的第i位的二进制数是什么 x>>k&1(前面的模板)
if(!son[p][u]) son[p][u]=++idx; ///如果插入中发现没有该子节点,开出这条路
p=son[p][u]; //指针指向下一层
}
}
int search(int x){
int p=0;int res=0;
for(int i=30;i>=0;i--){
int u=x>>i&1;
if(son[p][!u]) ////如果当前层有对应的不相同的数
{ ///p指针就指到不同数的地址
p=son[p][!u];
res=res*2+1;
///*2相当左移一位 然后如果找到对应位上不同的数res+1 例如 001
} /// 010
else //// --->011 //刚开始找0的时候是一样的所以+0 到了0和1的时候原来0右移一位,判断当前位是同还是异,同+0,异+1
{
p=son[p][u];
res=res*2+0;
}
}
return res;
}
int main(void){
cin.tie(0);
cin>>n;
idx=0;
for(int i=0;i<n;i++)
{
cin>>a[i];
insert(a[i]);
}
int res=0;
for(int i=0;i<n;i++)
{
res=max(res,search(a[i])); ///search(a[i])查找的是a[i]值的最大与或值
}
cout<<res<<endl;
}
2.9 并查集
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
const int N = 100010;
int n, m;
int p[N];
int find(int x){
if(p[x] != x)p[x] = find(p[x]);
return p[x];
}
int main(){
scanf("%d%d", &n, &m);
for(int i = 1; i <= n; i ++) p[i] = i;
while(m --){
char op[2];
int a, b;
scanf("%s%d%d", op, &a, &b);
if(op[0] == 'M') p[find(a)] = find(b);
else{
if(find(a) == find(b)) puts("Yes");
else puts("No");
}
}
return 0;
}
2.10 堆排序
#include <iostream>
#include <cstring>
#include <algorithm>
using namespace std;
const int N = 100010;
int a[N];
int n, m;
int r ;//堆右边界
void down(int u){
//t记录最小点的编号
int t = u;
//有左儿子,并且左儿子比t节点的值小,更新t
if(2 * u <= r && a[2 * u] < a[u]) t = 2 * u;
//有右儿子,并且右儿子比t节点的值小,更新t
if(2 * u + 1 <= r && a[2 * u + 1] < a[t]) t = 2 * u + 1;
//如果待调整点不是最小的
if(u != t){
//和最小的交换
swap(a[u], a[t]);
//递归处理
down(t);
}
}
int main(){
cin >> n >> m;
r = n;
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i ++ ) cin >> a[i];
for (int i = n / 2 ; i >= 1; i--) down(i);
while (m -- ) {
cout << a[1] << " ";
swap(a[1], a[r]);
r--;
down(1);
}
}
2.11 hash
2.11.1 拉链法
#include <iostream>
#include <cstring>
using namespace std;
const int N = 1e5 + 3;
int h[N], e[N], ne[N], idx;
void insert(int x) {
int k = (x % N + N) % N;
e[idx] = x;
ne[idx] = h[k];
h[k] = idx++;
}
int find(int x) {
int k = (x % N + N) % N;
for (int i = h[k]; i != -1; i = ne[i]) {
if (e[i] == x) return 1;
}
return 0;
}
int main() {
int n;
cin >> n;
memset(h, -1, sizeof h);
while (n--) {
string op;
int x;
cin >> op >> x;
if (op == "I") insert(x);
else {
if (find(x)) puts("Yes");
else puts("No");
}
}
return 0;
}
2.11.2 开放地址法
#include <cstring>
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
//开放寻址法一般开 数据范围的 2~3倍, 这样大概率就没有冲突了
const int N = 2e5 + 3;
const int null = 0x3f3f3f3f; //规定空指针为 null 0x3f3f3f3f
int h[N];
int find(int x) {
int t = (x % N + N) % N;
while (h[t] != null && h[t] != x) {
t++;
if (t == N) t = 0;
}
return t;
}
int n;
int main() {
cin >> n;
memset(h, 0x3f, sizeof h);
while (n--) {
string op;
int x;
cin >> op >> x;
if (op == "I") h[find(x)] = x;
else {
if (h[find(x)] == null) puts("No");
else puts("Yes");
}
}
return 0;
}
2.11.3 字符串哈希

#include<iostream>
#include<cstdio>
#include<string>
using namespace std;
typedef unsigned long long ULL;
const int N = 1e5+5,P = 131;//131 13331
ULL h[N],p[N];
// h[i]前i个字符的hash值
// 字符串变成一个p进制数字,体现了字符+顺序,需要确保不同的字符串对应不同的数字
// P = 131 或 13331 Q=2^64,在99%的情况下不会出现冲突
// 使用场景: 两个字符串的子串是否相同
ULL query(int l,int r){
return h[r] - h[l-1]*p[r-l+1];
}
int main(){
int n,m;
cin>>n>>m;
string x;
cin>>x;
//字符串从1开始编号,h[1]为前一个字符的哈希值
p[0] = 1;
h[0] = 0;
for(int i=0;i<n;i++){
p[i+1] = p[i]*P;
h[i+1] = h[i]*P +x[i]; //前缀和求整个字符串的哈希值
}
while(m--){
int l1,r1,l2,r2;
cin>>l1>>r1>>l2>>r2;
if(query(l1,r1) == query(l2,r2)) printf("Yes\n");
else printf("No\n");
}
return 0;
}
第三章 搜索与图论
3.1 DFS
3.1.1 图的DFS
void dfs(int u) {
st[u] = true;
for (int i = h[u]; i != -1; i = ne[i]) {
int j = e[i];
if (!st[j]) dfs(j);
}
}
using namespace std;
const int N = 1e5 + 10;
const int M = 2 * N;
int h[N],e[M],ne[M];
int idx, n;
int ans = N;
bool st[N];
void add(int a, int b) {
e[idx] = b, ne[idx] = h[a], h[a] = idx++;
}
//返回以u为根的子树中节点的个数,包括u节点
int dfs(int u) {
int res = 0; //存储 删掉某个节点之后,最大的连通子图节点数
st[u] = true;
int sum = 1;
for (int i = h[u]; i != -1; i = ne[i]) {
int j = e[i];
if (!st[j]) {
int s = dfs(j); // u节点的单棵子树节点数 如图中的size值
res = max(res, s);
sum += s;
}
}
//n-sum 如图中的n-size值,不包括根节点4;
res = max(res, n - sum); // 选择u节点为重心,最大的 连通子图节点数
ans = min(res, ans); //遍历过的假设重心中,最小的最大联通子图的 节点数
return sum;
}
int main() {
memset(h, -1, sizeof h);
cin >> n;
for (int i = 0; i < n - 1; i++) {
int a, b;
cin >> a >> b;
add(a, b), add(b, a);
}
dfs(1);
cout << ans << endl;
return 0;
}
3.1.2 回溯
import java.util.Scanner;
public class Main {
static int n;
static int N = 20;
static char[][] c;
static boolean col[] = new boolean[N],dg[] = new boolean[N],udg[] = new boolean[N];
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);
n = sc.nextInt();
c = new char[n][n];
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < n; j++) {
c[i][j]='.';
}
}
dfs(0);
}
static void dfs(int u){
if (u == n){
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
System.out.println(c[i]);
}
System.out.println();
}
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
if (!col[i] && !dg[i + u] && !udg[n + i - u]) {
c[u][i] = 'Q';
col[i] = dg[i + u] = udg[n + i - u] = true;
dfs(u+1);
col[i] = dg[i + u] = udg[n + i - u] = false;
c[u][i] = '.';
}
}
}
}
import java.util.Scanner;
public class Main {
static int n;
static int N = 20;
static char[][] c;
static boolean col[] = new boolean[N],dg[] = new boolean[N],udg[] = new boolean[N],row[] = new boolean[N];
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);
n = sc.nextInt();
c = new char[n][n];
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < n; j++) {
c[i][j]='.';
}
}
dfs(0,0,0);
}
static void dfs(int x,int y,int s){
if (y == n){
x++;
y = 0;
}
if (x == n){
if (s == n){
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) System.out.println(c[i]);
System.out.println();
}
return;
}
dfs(x,y+1,s);
if (!row[x] && !col[y] && !udg[x - y + n] && !dg[x + y]){
c[x][y] = 'Q';
row[x] = col[y] = dg[x + y] = udg[n + x - y] = true;
dfs(x ,y + 1,s + 1);
// dfs(x+1,0,s+1);
row[x] = col[y] = dg[x + y] = udg[n + x - y] = false;
c[x][y] = '.';
}
}
}
3.1.3 全排列
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
const int N = 10;
int path[N];
int state[N];
int n;
void dfs(int u){
if(u > n){
for(int i = 1; i <= n; i++)cout << path[i] << " ";
cout << endl;
}
for(int i = 1; i <= n; i++){
if(!state[i]){
path[u] = i;
state[i] = 1;
dfs(u + 1);
state[i] = 0;
}
}
}
int main(){
cin >> n;
dfs(1);
}
3.2 BFS
#include<iostream>
#include<cstring>
#include<algorithm>
using namespace std;
const int N = 110;
typedef pair<int, int> PII;
int n, m;
int g[N][N];
int d[N][N];
PII q[N * N];
int bfs(){
int hh = 0, tt = 0;
q[0] = {0, 0};
memset(d, - 1, sizeof d);
d[0][0] = 0;
int dx[4] = {-1, 0, 1, 0}, dy[4] = {0, 1, 0, -1};
while(hh <= tt){
PII t = q[hh++];
for(int i = 0; i < 4; i ++ ){
int x = t.first + dx[i], y = t.second + dy[i];
if(x >= 0 && x < n && y >= 0 && y < m && g[x][y] == 0 && d[x][y] == -1){
d[x][y] = d[t.first][t.second] + 1;
q[++tt] = {x, y};
}
}
}
return d[n - 1][m - 1];
}
int main() {
cin >> n >> m;
for(int i = 0; i < n; i ++ )
for(int j = 0; j < m; j ++ )
cin >> g[i][j];
cout << bfs() << endl;
return 0;
}
#include <iostream>
#include <cstring>
#include <algorithm>
#include <queue>
using namespace std;
const int N = 100010;
int h[N],ne[N], e[N], idx;
int dist[N];
int st[N];
int n, m;
void add(int a, int b){
e[idx] = b, ne[idx] = h[a], h[a] = idx++;
}
void bfs(){
memset(dist, 0x3f, sizeof(dist));
dist[1] = 0;
queue<int> q;
q.push(1);
st[1] = 1;
while(q.size()){
int t = q.front();
q.pop();
for(int i = h[t]; i != -1; i = ne[i]){
int j = e[i];
if(!st[j]){
dist[j] = dist[t] + 1;
q.push(j);
st[j] = 1;
}
}
}
}
int main(){
cin >> n >>m;
memset(h, -1, sizeof h);
for(int i = 0; i < m; i++){
int a, b;
cin >> a >> b;
add(a, b);
}
bfs();
cout << (dist[n] == 0x3f3f3f3f ? -1 : dist[n]);
return 0;
}
3.3 拓扑排序
#include <iostream>
#include <cstring>
using namespace std;
const int N = 100010;
int e[N], ne[N], h[N], idx, d[N], n, m;
int q[N], hh = 0, tt = -1;
void add(int a, int b) {
e[idx] = b, ne[idx] = h[a], h[a] = idx++;
}
void topsort() {
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++) if (d[i] == 0) q[++tt] = i;
while (tt >= hh) {
int a = q[hh++];
for (int i = h[a]; i != -1; i = ne[i]) {
int b = e[i];
d[b]--;
if (d[b] == 0) q[++tt] = b;
}
}
if (tt == n - 1) {
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) cout << q[i] << " ";
} else cout << -1;
}
int main() {
cin >> n >> m;
memset(h, -1, sizeof h);
while (m--) {
int a, b;
cin >> a >> b;
add(a, b);
d[b]++;
}
topsort();
return 0;
}
3.4 Dijkstra
#include <iostream>
#include <cstring>
#include <algorithm>
using namespace std;
const int N = 510;
int n, m;
int g[N][N];
int dist[N], st[N];
int dijkstra() {
memset(dist, 0x3f, sizeof dist);
dist[1] = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < n; ++i) {
int t = -1;
for (int j = 1; j <= n; ++j) {
if (!st[j] && (t == -1 || dist[j] < dist[t])) t = j;
}
st[t] = true;
for (int j = 1; j <= n; ++j) {
dist[j] = min(dist[j], dist[t] + g[t][j]);
}
}
if (dist[n] == 0x3f3f3f3f) return -1;
return dist[n];
}
int main() {
cin >> n >> m;
memset(g, 0x3f, sizeof g);
while (m--) {
int a, b, c;
scanf("%d%d%d", &a, &b, &c);
g[a][b] = min(g[a][b], c); //如果有重边,请保留权值最小的一条边
}
cout << dijkstra() << endl;
return 0;
}
int dijkstra() {
memset(dist, 0x3f, sizeof dist);
dist[1] = 0;
priority_queue<PII, vector<PII>, greater<PII>> heap;
heap.push({0, 1}); // 先将最短的距离添加到小根堆中
while (heap.size()) {
auto t = heap.top();
heap.pop();
int ver = t.second;
if (st[ver]) continue; // 如果已经被标记过,说明当前的点的边是比较长的重边,直接跳过。
st[ver] = true;
// 使用当前距离最短的点来更新其出边
for (int i = h[ver]; i != -1; i = ne[i]) {
int j = e[i]; // j 为 ver 出边所到达的点
if (dist[j] > dist[ver] + w[i]) {
dist[j] = dist[ver] + w[i];
// 将下一个距离源点最近的点添加到小根堆中
heap.push({dist[j], j});
}
}
}
if (dist[n] == 0x3f3f3f3f) return -1;
return dist[n];
}
3.5 Bellman-Ford
有边数限制的最短路
迪杰斯特拉是用最短的边去更新其他边,而spfa是上次更新的终点去更新其他边,贝尔曼则是非常暴力的每次更新所有边
import java.io.BufferedReader;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.io.InputStreamReader;
import java.util.Arrays;
public class Main {
static int N = 510;
static int M = 100010;
static int n;
static int m;
static int k;
static int[] dist = new int[N];
static Node[] list = new Node[M];
static int INF = 0x3f3f3f3f;
static int[] back = new int[N];
public static void bellman_ford(){
Arrays.fill(dist, INF);
dist[1] = 0;
for(int i = 0;i < k;i++){
back = Arrays.copyOf(dist, n + 1);//由于是从1开始存到n
for(int j = 0;j < m;j++) {
Node node = list[j];
int a = node.a;
int b = node.b;
int c = node.c;
dist[b] = Math.min(dist[b], back[a] + c);
}
}
if(dist[n] > INF/2) System.out.println("impossible");
else System.out.println(dist[n]);
}
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
BufferedReader reader = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(System.in));
String[] str1 = reader.readLine().split(" ");
n = Integer.parseInt(str1[0]);
m = Integer.parseInt(str1[1]);
k = Integer.parseInt(str1[2]);
for(int i = 0;i < m;i++){
String[] str2 = reader.readLine().split(" ");
int a = Integer.parseInt(str2[0]);
int b = Integer.parseInt(str2[1]);
int c = Integer.parseInt(str2[2]);
list[i] = new Node(a,b,c);
}
bellman_ford();
}
}
class Node{
int a, b, c;
public Node(int a,int b,int c){
this.a = a;
this.b = b;
this.c = c;
}
}
3.6 spfa
#include <iostream>
#include <algorithm>
#include <cstring>
using namespace std;
const int N = 100010;
int h[N], e[N], w[N], ne[N], idx;
int st[N];
int dist[N];
int q[N], hh, tt = -1;
void add(int a, int b, int c){
e[idx] = b, w[idx] = c, ne[idx] = h[a], h[a] = idx++;
}
void spfa(){
q[++tt] = 1;//从1号顶点开始松弛,1号顶点入队
dist[1] = 0;
st[1] = 1;//1号顶点在队列中
while(tt >= hh){//不断进行松弛
int a = q[hh++];
st[a] = 0;//取完队头后,a不在队列中了
for(int i = h[a]; i != -1; i = ne[i]){
int b = e[i], c = w[i];
if(dist[b] > dist[a] + c){
dist[b] = dist[a] + c;
if(!st[b]){//如果没在队列中
q[++tt] = b;//入队
st[b] = 1;//打标记
}
}
}
}
}
int main(){
memset(h, -1, sizeof h);
memset(dist, 0x3f, sizeof dist);
int n, m;
cin >> n >> m;
for(int i = 0; i < m; i++){
int a, b, w;
cin >> a >> b >> w;
add(a, b, w);
}
spfa();
if(dist[n] == 0x3f3f3f3f ) cout << "impossible";
else cout << dist[n];
return 0;
}
3.7 Floyd
import java.util.Scanner;
public class Main {
static int N = 210;
static int n, m, q;
static int[][] d = new int[N][N];
static int INF = (int)1e9;
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);
n = sc.nextInt(); m = sc.nextInt(); q = sc.nextInt();
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++) {
for (int j = 1; j <= n; j++) {
if (i == j) d[i][j] = 0;
else d[i][j] = INF;
}
}
for(int i = 0; i < m; i++) {
int a = sc.nextInt(), b = sc.nextInt(), w = sc.nextInt();
d[a][b] = Math.min(d[a][b], w);
}
Floyd();
while (q-- > 0) {
int a = sc.nextInt(), b = sc.nextInt();
if (d[a][b] > INF / 2) System.out.println("impossible");
else System.out.println(d[a][b]);
}
}
private static void Floyd() {
for (int k = 1; k <= n; k++) {
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++) {
for (int j = 1; j <= n; j++) {
d[i][j] = Math.min(d[i][j], d[i][k] + d[k][j]);
}
}
}
}
}
3.8 Prim
import java.util.Arrays;
import java.util.Scanner;
public class Main {
static int N = 510, INF = 0x3f3f3f3f;
static int n, m;
static int [][] g = new int[N][N];
static int [] dist = new int[N];
static boolean[] st = new boolean[N];
private static int prime() {
Arrays.fill(dist, INF);
int res = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < n; i ++) {
int t = -1;
for (int j = 1; j <= n; j ++) {
if (!st[j] && (t == -1 || dist[t] > dist[j])) {
t = j;
}
}
if (i != 0 && dist[t] == INF) return INF;
if (i != 0) res += dist[t];
for (int j = 1; j <= n; j ++) dist[j] = Math.min(dist[j], g[t][j]);
st[t] = true;
}
return res;
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);
n = sc.nextInt();
m = sc.nextInt();
for (int i = 0; i < N; i++) Arrays.fill(g[i], INF);
while (m -- > 0) {
int a = sc.nextInt();
int b = sc.nextInt();
int c = sc.nextInt();
g[a][b] = g[b][a] = Math.min(g[a][b], c);
}
int t = prime();
if (t == INF) System.out.println("impossible");
else System.out.println(t);
}
}
3.9 Kruskal
#include <iostream>
#include <cstring>
#include <algorithm>
using namespace std;
const int N = 100010;
int p[N];//保存并查集
struct E{
int a;
int b;
int w;
bool operator < (const E& rhs){
return this->w < rhs.w;
}
}edg[N * 2];
int res = 0;
int n, m;
int cnt = 0;
int find(int a){//并查集找祖宗
if(p[a] != a) p[a] = find(p[a]);
return p[a];
}
void klskr(){
for(int i = 1; i <= m; i++) {
int pa = find(edg[i].a);// a 点所在的集合
int pb = find(edg[i].b);// b 点所在的集合
if(pa != pb){//如果 a b 不在一个集合中
res += edg[i].w;//a b 之间这条边要
p[pa] = pb;// 合并a b
cnt ++; // 保留的边数量+1
}
}
}
int main(){
cin >> n >> m;
for(int i = 1; i <= n; i++) p[i] = i;
for(int i = 1; i <= m; i++){
int a, b , c;
cin >> a >> b >>c;
edg[i] = {a, b, c};
}
sort(edg + 1, edg + m + 1);
klskr();
if(cnt < n - 1) {
cout<< "impossible";
return 0;
}
cout << res;
return 0;
}
第四章 数学知识
4.1 质数
4.1.1 判断质数
试除法判断质数
import java.util.Scanner;
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);
int n = sc.nextInt();
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
int a = sc.nextInt();
if (is_prime(a)) System.out.println("Yes");
else System.out.println("No");
}
}
static boolean is_prime(int n){
if (n <= 1) return false;
for (int i = 2; i <= n/i ; i++) {
if (n % i == 0) return false;
}
return true;
}
}
4.1.2 分解质因数
import java.util.Scanner;
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);
int n = sc.nextInt();
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
int a = sc.nextInt();
divided(a);
}
}
static void divided(int n){
for (int i = 2; i <= n/i; i++) {
if (n % i == 0){
int s = 0;
while (n % i == 0){
n /= i;
s++;
}
System.out.println(i+" "+s);
}
}
if (n > 1) System.out.println(n+" "+1);
System.out.println();
}
}
4.1.3 筛质数
import java.util.Scanner;
public class acwing868_1 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);
int n = sc.nextInt();
boolean[] b = new boolean[n];
int cnt = 0;
for (int i = 2; i <= n; i++) {
if (!b[i]){
cnt++;
for (int j = i; j <= n; j += i) b[j] = true;
}
}
System.out.println(cnt);
}
}
import java.util.Scanner;
public class acwing868_2 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);
int n = sc.nextInt();
boolean[] st = new boolean[n];
int[] primes = new int[n];
int cnt = 0;
//外层从2~n迭代,因为这毕竟算的是1~n中质数的个数,而不是某个数是不是质数的判定
for(int i=2;i<=n;i++){
if(!st[i]) primes[cnt++]=i;
for(int j=0;primes[j]<=n/i;j++){//primes[j]<=n/i:变形一下得到——primes[j]*i<=n,把大于n的合数都筛了就
//没啥意义了
st[primes[j]*i]=true;//用最小质因子去筛合数
//1)当i%primes[j]!=0时,说明此时遍历到的primes[j]不是i的质因子,那么只可能是此时的primes[j]<i的
//最小质因子,所以primes[j]*i的最小质因子就是primes[j];
//2)当有i%primes[j]==0时,说明i的最小质因子是primes[j],因此primes[j]*i的最小质因子也就应该是
//prime[j],之后接着用st[primes[j+1]*i]=true去筛合数时,就不是用最小质因子去更新了,因为i有最小
//质因子primes[j]<primes[j+1],此时的primes[j+1]不是primes[j+1]*i的最小质因子,此时就应该
//退出循环,避免之后重复进行筛选。
if(i%primes[j]==0) break;
}
}
System.out.println(cnt);
}
}
4.2 约数
4.2.1 试除法求约数
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.Arrays;
import java.util.Collections;
import java.util.Scanner;
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);
int T = sc.nextInt();
while (T-- != 0){
int n = sc.nextInt();
ArrayList<Integer> arr = new ArrayList<>();
for (int i = 1; i <= n/i; i++) {
if (n % i == 0){
arr.add(i);
if (i != n/i){
arr.add(n/i);
}
}
}
Collections.sort(arr);
for (int i = 0; i < arr.size(); i++) System.out.print(arr.get(i) + " ");
System.out.println();
}
}
}
4.2.2 约数个数
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
typedef long long LL;
const int mod = 1e9 + 7;
int main(){
int n,x;
LL ans = 1;
unordered_map<int,int> hash;
cin >> n;
while(n--){
cin >> x;
for(int i = 2;i <= x/i; ++i){
while(x % i == 0){
x /= i;
hash[i] ++;
}
}
if(x > 1) hash[x] ++;
}
for(auto i : hash) ans = ans*(i.second + 1) % mod;
cout << ans;
return 0;
}
4.2.3 约数之和
#include <iostream>
#include <algorithm>
#include <unordered_map>
#include <vector>
using namespace std;
typedef long long LL;
const int N = 110, mod = 1e9 + 7;
int main(){
int n;
cin >> n;
unordered_map<int, int> primes;
while (n -- ){
int x;
cin >> x;
for (int i = 2; i <= x / i; i ++ )
while (x % i == 0) {
x /= i;
primes[i] ++ ;
}
if (x > 1) primes[x] ++ ;
}
LL res = 1;
for (auto p : primes) {
LL a = p.first, b = p.second;
LL t = 1;
while (b -- ) t = (t * a + 1) % mod;
res = res * t % mod;
}
cout << res << endl;
return 0;
}
4.2.4 最大公约数
欧几里得算法(辗转相除法)
#include <iostream>
#include <algorithm>
using namespace std;
int main(){
int T;
cin >> T;
while(T--){
int a, b;
cin >> a >> b;
while(a % b) {
int c = a % b;
a = b;
b = c;
}
cout << b << endl;
}
}
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
int n;
int gcd(int a, int b){
return b ? gcd(b, a % b) : a;
}
int main(){
cin >> n;
while (n--) {
int a, b;
scanf("%d%d", &a, &b);
printf("%d\n", gcd(a, b));
}
return 0;
}
4.3 欧拉函数
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
typedef long long ll;
int main(){
ll k;cin>>k;
while(k--) {
ll x;
cin>>x;
ll res=x;
for(ll i=2;i<=x/i;i++)
if(x%i==0) {
while(x%i==0)x/=i;
res=res/i*(i-1); //注意先除再乘 N/pk*(pk-1);
}
if(x>1)res=res/x*(x-1);
cout<<res<<endl;
}
}
筛法求欧拉函数
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
typedef long long LL;
const int N = 1000010;
int primes[N], euler[N], cnt;
bool st[N];
void getSumEuler(int n){
euler[1] = 1;
for(int i = 2; i <= n; i++){
if(!st[i]){
primes[cnt++] = i;
euler[i] = i - 1;
}
for(int j = 0; primes[j] <= n / i; j++){
int t = primes[j] * i;
st[t] = true;
if(i % primes[j] == 0){
euler[t] = euler[i] * primes[j];
break;
}
euler[t] = euler[i] * (primes[j] - 1);
}
}
}
int main(){
int n;
cin >> n;
getSumEuler(n);
LL res = 0;
for(int i = 1; i <= n; i++) res += euler[i];
cout << res << endl;
return 0;
}
4.4 快速幂
4.4.1 快速幂
import java.util.Scanner;
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);
int T = sc.nextInt();
while (T-- != 0){
int a = sc.nextInt();
int b = sc.nextInt();
int p = sc.nextInt();
System.out.println(qmi(a,b,p));
}
}
static int qmi(int a,int b,int p){
int res = 1;
while (b != 0){
if ((b & 1) == 1) res = (int)((long)res * a % p);
a = (int)((long)a * a % p);
b >>= 1;
}
return res;
}
}
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
long long qmi(long long a,int b,int p){
long long res=1;
while(b){
if(b&1) res = res *a %p;
b>>=1;
a=a*a%p;
}
return res;
}
int main(){
int n;
cin>>n;
while(n--){
cin.tie(0);
ios::sync_with_stdio(false);
int a,b,p;
long long res=1;
cin>>a>>b>>p;
res = qmi(a,b,p);
cout<<res<<endl;
}
return 0;
}
4.4.2 快速幂求逆元
import java.util.Scanner;
public class acwing876 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);
int T = sc.nextInt();
while (T-- != 0){
int a = sc.nextInt();
int p = sc.nextInt();
int res = qmi(a, p - 2, p);
if (a % p != 0) System.out.println(res);
else System.out.println("impossible");
}
}
static int qmi(int a,int b,int p){
int res = 1;
while (b != 0){
if ((b & 1) == 1) res = (int)((long)res * a % p);
a = (int)((long)a * a % p);
b >>= 1;
}
return res;
}
}
4.5 扩展欧几里得算法
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
int exgcd(int a, int b, int &x, int &y){
if(b==0){
x = 1, y = 0;
return a;
}
int x1,y1,gcd;
gcd = exgcd(b, a%b, x1, y1);
x = y1, y = x1 - a/b*y1;
return gcd;
}
int main(){
int n,a,b,x,y;
cin>>n;
while(n--){
cin>>a>>b;
exgcd(a,b,x,y);
cout<<x<<" "<<y<<endl;
}
return 0;
}
4.6 求组合数
4.6.1 求组合数1
import java.util.Scanner;
public class Main {
static int mod = 1000000007;
static long[][] c = new long[2010][2010];
static void init(){
for(int i = 0;i <= 2001;i++) {
for(int j = 0;j <= i;j++) {
if(j == 0) c[i][j] = 1;
else c[i][j] = (c[i-1][j-1] + c[i-1][j]) % mod;
}
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
init();
Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);
int n = sc.nextInt();
while (n-- != 0){
int a = sc.nextInt();
int b = sc.nextInt();
System.out.println(c[a][b]);
}
}
}
4.6.2 求组合数2
import java.util.*;
import java.io.*;
class Main{
static int N = 100010, n = 0, MOD = 1000000007;
static int[] fact = new int[N], infact = new int[N];
static int qmi(int a, int k, int p){
int res = 1;
while(k != 0){
if((k & 1) != 0)res = (int)((long)res * a % p);
a = (int)((long)a * a % MOD);
k >>= 1;
}
return res;
}
public static void main(String[] args)throws Exception{
BufferedReader buf = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(System.in));
n = Integer.valueOf(buf.readLine());
fact[0] = infact[0] = 1;
for(int i = 1; i < N; ++i){
fact[i] = (int)((long)fact[i - 1] * i % MOD);
infact[i] = (int)((long)infact[i - 1] * qmi(i, MOD - 2, MOD) % MOD);
}
while(n -- != 0){
String[] info = buf.readLine().split(" ");
int a = Integer.valueOf(info[0]);
int b = Integer.valueOf(info[1]);
System.out.println((int)((long)((long)fact[a] * infact[a - b] % MOD) * infact[b] % MOD));
}
}
}
4.7 博弈论
#include <iostream>
#include <cstdio>
using namespace std;
/*
先手必胜状态:先手操作完,可以走到某一个必败状态
先手必败状态:先手操作完,走不到任何一个必败状态
先手必败状态:a1 ^ a2 ^ a3 ^ ... ^an = 0
先手必胜状态:a1 ^ a2 ^ a3 ^ ... ^an ≠ 0
*/
int main(){
int n;
scanf("%d", &n);
int res = 0;
for(int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
int x;
scanf("%d", &x);
res ^= x;
}
if(res == 0) puts("No");
else puts("Yes");
}
树状数组
import java.util.Scanner;
public class Main {
static int lowbit(int x) {
return x & -x;
}
static int n;
// 更新树状数组
static void add(int x, int v) {
for (int i = x; i <= n; i += lowbit(i)) tree[i] += v; // 更新树状数组
}
// 计算前缀和
static int query(int x) {
int res = 0;
for (int i = x; i > 0; i -= lowbit(i)) res += tree[i]; // 计算前缀和
return res;
}
static int N = 100010;
static int[] a = new int[N];
static int[] tree = new int[N];
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);
n = sc.nextInt();
int m = sc.nextInt();
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++) a[i] = sc.nextInt();
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++) add(i,a[i]);
while (m-- != 0){
int k = sc.nextInt();
int x = sc.nextInt();
int y = sc.nextInt();
if (k == 0){
System.out.println(query(y)-query(x-1));
}else {
add(x,y);
}
}
}
}
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
const int N=100009;
int a[N],tr[N];
int n,m;
//每个数的间隔,背下来就行
int lowbit(int x)
{
return x&-x;
}
//第x个数加上v
int add(int x,int v)
{
//因为树状数组的性质,加一个数,只影响logn个数,所有不用全加完
//从当前位置开始加,每个间隔是lowbit(i),一直加到最后
for(int i=x;i<=n;i+=lowbit(i))
tr[i]+=v;
}
//返回x的前缀和
int qurry(int x)
{
//因为树状数组的性质,求前缀和,只用加logn个数,所有不用全加完
//从当前位置开始累加,每个间隔是lowbit(i),一直加到i==0停止
int cnt=0;
for(int i=x;i!=0;i-=lowbit(i))
cnt+=tr[i];
return cnt;
}
int main()
{
cin>>n>>m;
for(int i=1;i<=n;i++)
scanf("%d",&a[i]);
for(int i=1;i<=n;i++)
add(i,a[i]);//第i个数加上a[i]
while(m--){
int k,x,y;
scanf("%d%d%d",&k,&x,&y);
if(k==0) printf("%d\n",qurry(y)-qurry(x-1));
else add(x,y);
}
return 0;
}
第五章 动态规划
5.1 背包问题
5.1.1 01背包问题
import java.util.Scanner;
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);
int n = sc.nextInt();
int m = sc.nextInt();
int[] a = new int[n + 1];
int[] v = new int[n + 1];
int[][] dp = new int[n + 1][m + 1];
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++) {
v[i] = sc.nextInt();
a[i] = sc.nextInt();
}
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++) {
for (int j = 1; j <= m; j++) {
if (j < v[i]) dp[i][j] = dp[i-1][j];
else dp[i][j] = Math.max(dp[i-1][j],dp[i-1][j-v[i]]+a[i]);
}
}
System.out.println(dp[n][m]);
}
}
import java.util.Scanner;
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);
int n = sc.nextInt();
int m = sc.nextInt();
int[] a = new int[n + 1];
int[] v = new int[n + 1];
int[] dp = new int[m + 1];
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++) {
v[i] = sc.nextInt();
a[i] = sc.nextInt();
}
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++) {
for (int j = m; j >= v[i]; j--) dp[j] = Math.max(dp[j], dp[j - v[i]] + a[i]);
}
System.out.println(dp[m]);
}
}
5.1.2 完全背包问题
import java.util.Scanner;
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);
int n = sc.nextInt();
int m = sc.nextInt();
int[] a = new int[n + 1];
int[] v = new int[n + 1];
int[] dp = new int[m + 1];
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++) {
v[i] = sc.nextInt();
a[i] = sc.nextInt();
}
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++) {
for (int j = v[i]; j <= m; j++) dp[j] = Math.max(dp[j], dp[j - v[i]] + a[i]);
}
System.out.println(dp[m]);
}
}
import java.util.Scanner;
public class acwing3_1 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);
int n = sc.nextInt();
int m = sc.nextInt();
int[] a = new int[n + 1];
int[] v = new int[n + 1];
int[][] dp = new int[n + 1][m + 1];
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++) {
v[i] = sc.nextInt();
a[i] = sc.nextInt();
}
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++) {
for (int j = 1; j <= m; j++) {
dp[i][j] = dp[i-1][j];
if (j >= v[i]){
dp[i][j] = Math.max(dp[i-1][j],dp[i][j-v[i]]+a[i]);
}
}
}
System.out.println(dp[n][m]);
}
}
5.2 线性DP
5.2.2 最长上升子序列
import java.util.Scanner;
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);
int n = sc.nextInt();
int[] a = new int[n+1];
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++) a[i] = sc.nextInt();
int[] dp = new int[n+1];
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++) {
dp[i] = 1;
for (int j = 1; j < i; j++) {
if (a[j] < a[i]) dp[i] = Math.max(dp[i], dp[j] + 1);
}
}
int max = 1;
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++) max = Math.max(max,dp[i]);
System.out.println(max);
}
}
5.2.3 最长公共子序列
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
const int N = 1010;
int n, m;
char a[N], b[N];
int f[N][N];
int main() {
cin >> n >> m >> a + 1 >> b + 1;
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++) {
for (int j = 1; j <= m; j++) {
if (a[i] == b[j]) f[i][j] = f[i - 1][j - 1] + 1;
else f[i][j] = max(f[i - 1][j], f[i][j - 1]);
}
}
cout << f[n][m] << '\n';
return 0;
}
import java.util.Scanner;
public class acwing897{
public static final int N = 1010;
public static void main(String[] args){
Scanner scan = new Scanner(System.in);
int n = scan.nextInt();
int m = scan.nextInt();
char[] a = scan.next().toCharArray();
char[] b = scan.next().toCharArray();
int[][] dp = new int[N][N];
for(int i = 1; i <= n; i++){
for(int j = 1; j <= m; j++){
dp[i][j] = Math.max(dp[i-1][j], dp[i][j-1]);
if(a[i-1] == b[j-1]){
dp[i][j] = Math.max(dp[i][j], dp[i-1][j-1] + 1);
}
}
}
System.out.println(dp[n][m]);
}
}
5.3 区间DP
package base.fifth;
import java.util.Scanner;
public class acwing282 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);
int n = sc.nextInt();
int[] a = new int[n + 1];
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++) a[i] = sc.nextInt() + a[i - 1];
int[][] dp = new int[n + 1][n + 1];
for (int len = 2; len <= n; len++) {
for (int i = 1; i + len - 1 <= n; i++) {
int j = i + len - 1;
dp[i][j] = Integer.MAX_VALUE;
for (int k = i; k < j; k++) {
dp[i][j] = Math.min(dp[i][j], dp[i][k] + dp[k + 1][j] + a[j] - a[i - 1]);
}
}
}
System.out.println(dp[1][n]);
}
}
5.6 状态压缩DP
AcWing 291. 蒙德里安的梦想
#include<iostream>
#include<cstring>
using namespace std;
//数据范围1~11
const int N = 12;
//每一列的每一个空格有两种选择,放和不放,所以是2^n
const int M = 1 << N;
//方案数比较大,所以要使用long long 类型
//f[i][j]表示 i-1列的方案数已经确定,从i-1列伸出,并且第i列的状态是j的所有方案数
long long f[N][M];
//第 i-2 列伸到 i-1 列的状态为 k , 是否能成功转移到 第 i-1 列伸到 i 列的状态为 j
//st[j|k]=true 表示能成功转移
bool st[M];
//n行m列
int n, m;
int main() {
// 预处理st数组
while (cin >> n >> m, n || m) {
for (int i = 0; i < 1 << n; i++) {
// 第 i-2 列伸到 i-1 列的状态为 k ,
// 能成功转移到
// 第 i-1 列伸到 i 列的状态为 j
st[i] = true;
// 记录一列中0的个数
int cnt = 0;
for (int j = 0; j < n; j++) {
// 通过位操作,i状态下j行是否放置方格,
// 0就是不放, 1就是放
if (i >> j & 1) {
// 如果放置小方块使得连续的空白格子数成为奇数,
// 这样的状态就是不行的,
if (cnt & 1) {
st[i] = false;
break;
}
}else cnt++;
// 不放置小方格
}
if (cnt & 1) st[i] = false;
}
// 初始化状态数组f
memset(f, 0, sizeof f);
// 棋盘是从第0列开始,没有-1列,所以第0列第0行,不会有延伸出来的小方块
// 没有横着摆放的小方块,所有小方块都是竖着摆放的,这种状态记录为一种方案
f[0][0] = 1;
// 遍历每一列
for (int i = 1; i <= m; i++) {
// 枚举i列每一种状态
for (int j = 0; j < 1 << n; j++) {
// 枚举i-1列每一种状态
for (int k = 0; k < 1 << n; k++) {
// f[i-1][k] 成功转到 f[i][j]
if ((j & k) == 0 && st[j | k]) {
f[i][j] += f[i - 1][k]; //那么这种状态下它的方案数等于之前每种k状态数目的和
}
}
}
}
// 棋盘一共有0~m-1列
// f[i][j]表示 前i-1列的方案数已经确定,从i-1列伸出,并且第i列的状态是j的所有方案数
// f[m][0]表示 前m-1列的方案数已经确定,从m-1列伸出,并且第m列的状态是0的所有方案数
// 也就是m列不放小方格,前m-1列已经完全摆放好并且不伸出来的状态
cout << f[m][0] << endl;
}
return 0;
}
AcWing 91. 最短Hamilton路径
#include<iostream>
#include<cstring>
#include<algorithm>
using namespace std;
const int N=20,M=1<<N;
int f[M][N],w[N][N];//w表示的是无权图
int main()
{
int n;
cin>>n;
for(int i=0;i<n;i++)
for(int j=0;j<n;j++)
cin>>w[i][j];
memset(f,0x3f,sizeof(f));//因为要求最小值,所以初始化为无穷大
f[1][0]=0;//因为零是起点,所以f[1][0]=0;
for(int i=0;i<1<<n;i++)//i表示所有的情况
for(int j=0;j<n;j++)//j表示走到哪一个点
if(i>>j&1)
for(int k=0;k<n;k++)//k表示走到j这个点之前,以k为终点的最短距离
if(i>>k&1)
f[i][j]=min(f[i][j],f[i-(1<<j)][k]+w[k][j]);//更新最短距离
cout<<f[(1<<n)-1][n-1]<<endl;//表示所有点都走过了,且终点是n-1的最短距离
//位运算的优先级低于'+'-'所以有必要的情况下要打括号
return 0;
}
5.? 树形DP
package base.fifth;
import java.util.Arrays;
import java.util.Scanner;
public class acwing285 {
static int N = 6010;
static int[] happy = new int[N];
static int[] h = new int[N];
static int[] e = new int[N];
static int[] ne = new int[N];
static boolean[] has_father = new boolean[N];
static int idx;
static int[][] dp = new int[N][2];
static void add(int a, int b) {
e[idx] = b;
ne[idx] = h[a];
h[a] = idx++;
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);
int n = sc.nextInt();
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++) happy[i] = sc.nextInt();
Arrays.fill(h, -1);
for (int i = 0; i < n - 1; i++) {
int a = sc.nextInt();
int b = sc.nextInt();
has_father[a] = true;
add(b,a);
}
int root = 1;
while (has_father[root]) root++;
dfs(root);
System.out.println(Math.max(dp[root][0],dp[root][1]));
}
static void dfs(int u) {
dp[u][1] = happy[u];
for (int i = h[u]; i != -1; i = ne[i]) {
int j = e[i];
dfs(j);
dp[u][0] += Math.max(dp[j][1], dp[j][0]);
dp[u][1] += dp[j][0];
}
}
}
第六章 贪心
import java.util.*;
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner scanner = new Scanner(System.in);
int m = scanner.nextInt();
int s = scanner.nextInt();
int c = scanner.nextInt();
int[] cow = new int[c];
Integer[] T = new Integer[c - 1];
for (int i = 0; i < c; i++) cow[i] = scanner.nextInt();
if (c <= m) {
System.out.println(c);
return;
}
Arrays.sort(cow);
int ans = cow[c - 1] - cow[0] + 1;
for (int i = 0; i < c - 1; i++) T[i] = cow[i + 1] - cow[i] - 1;
Arrays.sort(T, new Comparator<Integer>() {
@Override
public int compare(Integer o1, Integer o2) {
return o2 - o1;
}
});
for (int i = 0; i < m - 1; i++) ans -= T[i];
System.out.println(ans);
}
}
import java.util.*;
public class Main {
static final int maxn = 210;
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner scanner = new Scanner(System.in);
int m = scanner.nextInt();
int s = scanner.nextInt();
int c = scanner.nextInt();
int[] cow = new int[maxn];
Integer[] T = new Integer[maxn];
for (int i = 1; i <= c; i++) cow[i] = scanner.nextInt();
if (c <= m) {
System.out.println(c);
return;
}
Arrays.sort(cow, 1, c + 1);
int ans = cow[c] - cow[1] + 1;
for (int i = 1; i <= c - 1; i++) T[i] = cow[i + 1] - cow[i] - 1;
Arrays.sort(T, 1, c, new Comparator<Integer>() {
@Override
public int compare(Integer o1, Integer o2) {
return o2 - o1;
}
});
for (int i = 1; i < m; i++) ans -= T[i];
System.out.println(ans);
}
}
- 感谢你赐予我前进的力量
赞赏者名单
因为你们的支持让我意识到写文章的价值🙏
本文是原创文章,采用 CC BY-NC-ND 4.0 协议,完整转载请注明来自 Matriy
评论
匿名评论
隐私政策
你无需删除空行,直接评论以获取最佳展示效果




